封装信息
| CAD 模型: | View CAD Model |
| Pkg. Type: | FBGA |
| Pkg. Code: | VDE |
| Lead Count (#): | 196 |
| Pkg. Dimensions (mm): | 15.0 x 15.0 x 1.02 |
| Pitch (mm): | 1 |
环境和出口类别
| Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) | 3 |
| Pb (Lead) Free | No |
| ECCN (US) | |
| HTS (US) |
产品属性
| Pkg. Type | FBGA |
| Carrier Type | Tray |
| MOQ | 126 |
| Clock Rate (MHz) | 95 |
| Data | 16 Bits |
| Decimation Factors | 4 to gt 16k |
| Filtering | CIC HB Programmable FIR Re-Sampler |
| Lead Count (#) | 196 |
| Length (mm) | 15 |
| Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) | 3 |
| Pb (Lead) Free | No |
| Pb Free Category | Solder Ball Terminal |
| Pitch (mm) | 1 |
| Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | 15.0 x 15.0 x 1.02 |
| Qualification Level | Standard |
| Temp. Range (°C) | -40 to +85°C |
| Thickness (mm) | 1.02 |
| Width (mm) | 15 |
有关 ISL5216 的资源
描述
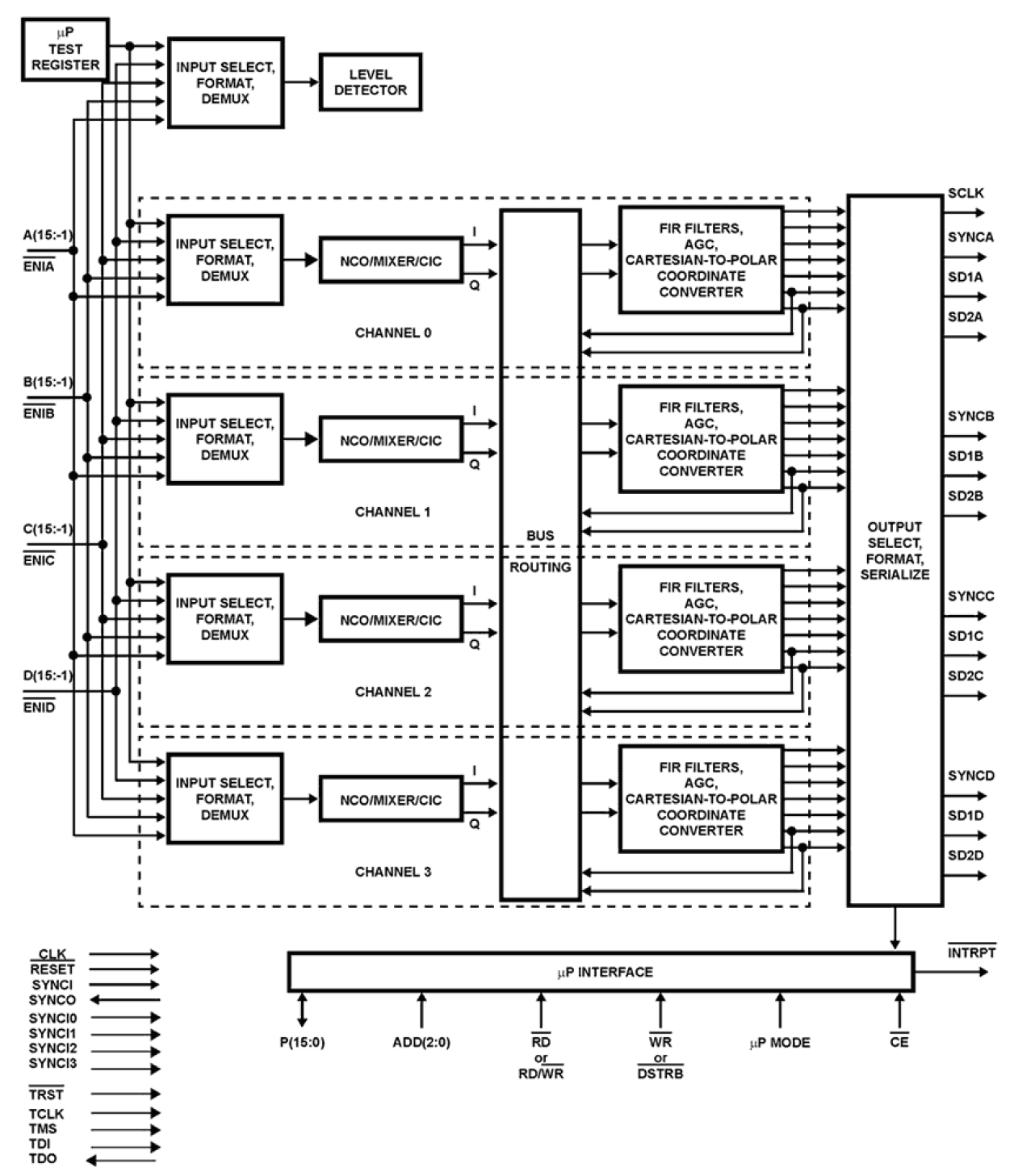
The ISL5216 Quad Programmable Digital Downconverter (QPDC) is designed for high dynamic range applications such as cellular basestations where multiple channel processing is required in a small physical space. The QPDC combines into a single package a set of four channels which include: digital mixers, a quadrature carrier NCO, digital filters, a resampling filter, a cartesian to polar coordinate converter, and an automatic gain control (AGC) loop. The ISL5216 accepts four channels of 16-bit fixed or up to 14-bit mantissa/3-bit exponent floating point real or complex digitized IF samples which are mixed with local quadrature sinusoids. Each channel carrier NCO frequency is set independently by the microprocessor. The output of the mixers is filtered with CIC and FIR filters, with a variety of decimation options. Gain adjustment is provided on the filtered signal. The digital AGC provides a gain adjust range of up to 96dB with programmable thresholds and slew rates. A cartesian to polar coordinate converter provides magnitude and phase outputs. A frequency discriminator is also provided to allow FM demodulation. Selectable outputs include I samples, Q samples, magnitude, phase, frequency, and AGC gain. The output resolution is selectable from a 4-bit fixed point to a 32-bit floating point. Output bandwidths in excess of 1MHz are achievable using a single channel. Wider bandwidths are available by cascading or polyphasing multiple channels.