特性
- 1 – 0.7V current mode differential HCSL output pair
- Low additive jitter
- suitable for use in PCIe Gen2 and Gen3 systems
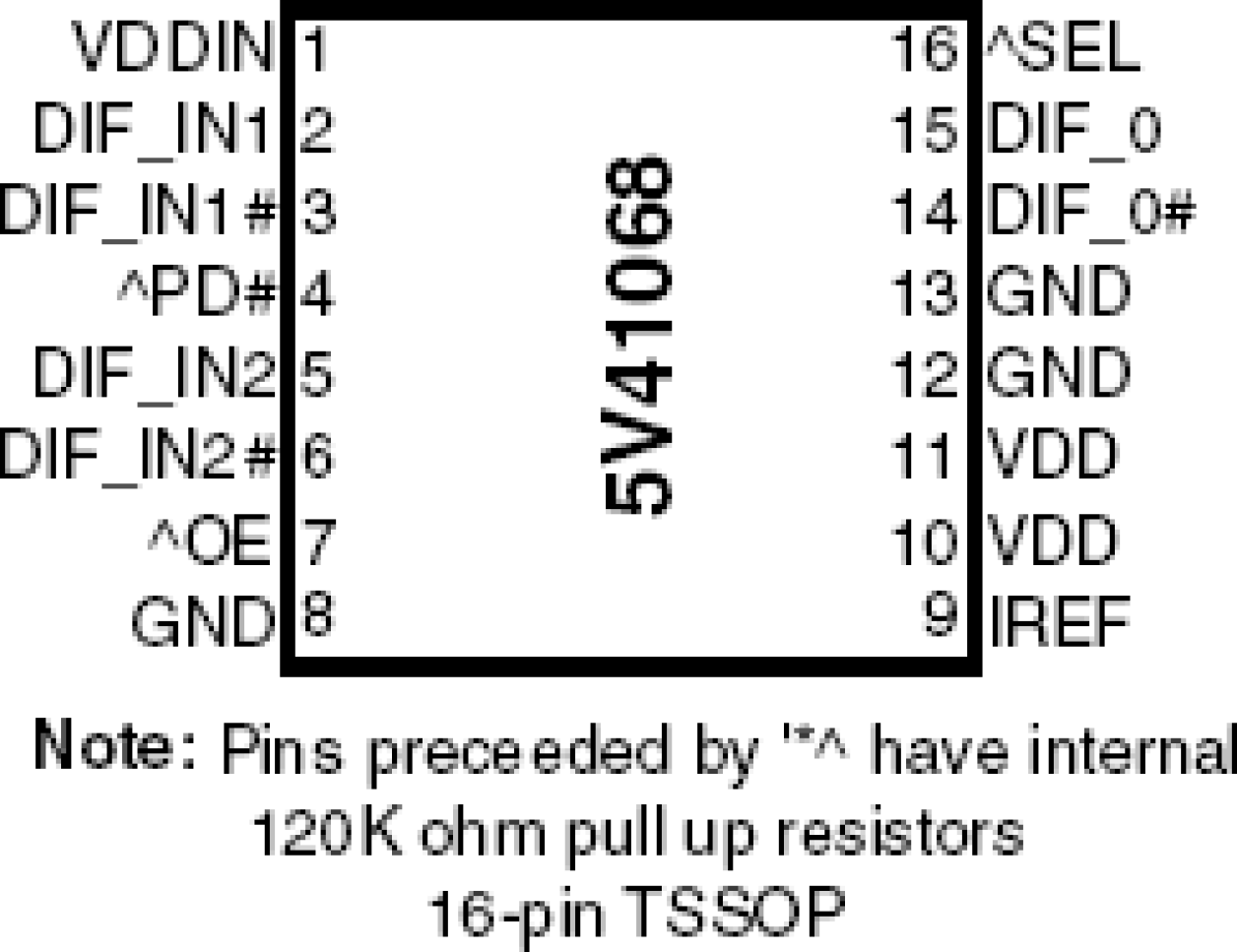
- 16-pin TSSOP package
- small board footprint
- Outputs can be terminated to LVDS
- can drive a wider variety of devices
- OE control pin
- greater system power management
- Industrial temperature range available
- supports demanding embedded applications
- Additive cycle-to-cycle jitter <5 ps
- Additive phase jitter (PCIe Gen3) <0.2ps
- Operating frequency up to 200MHz
描述
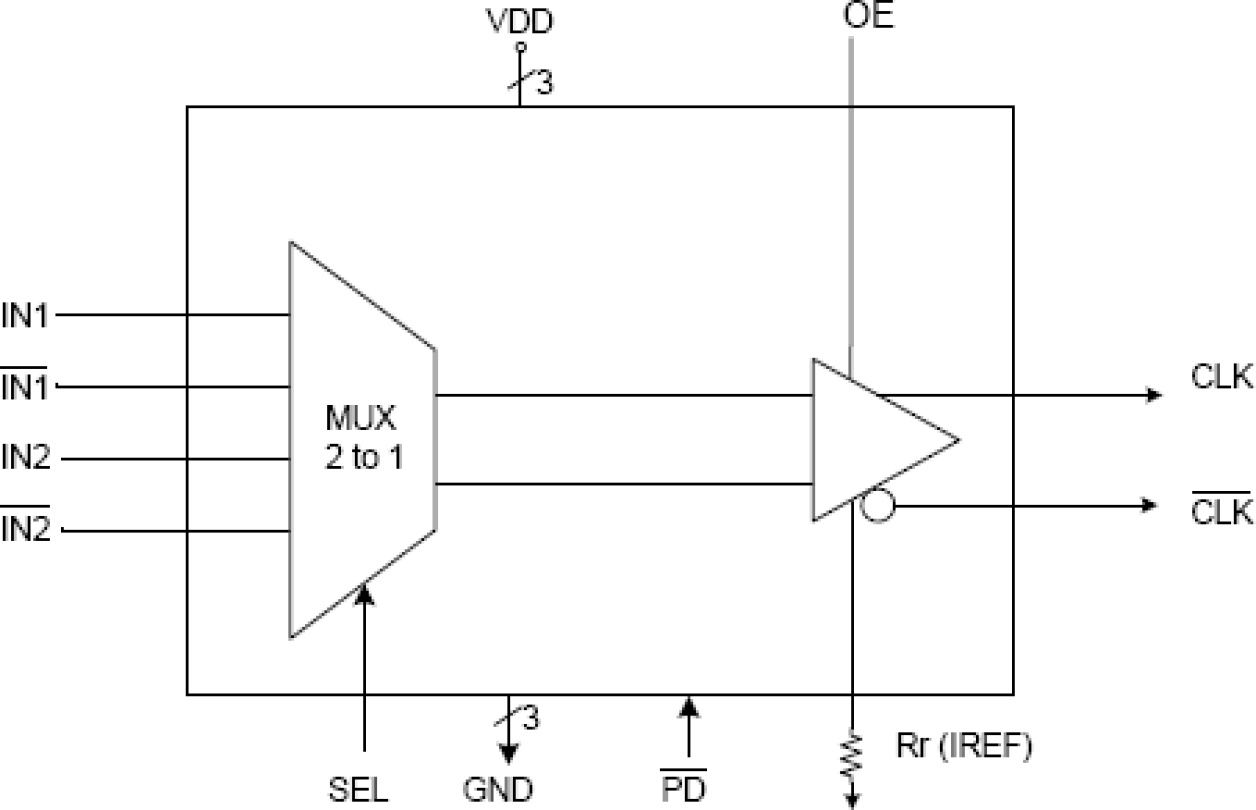
The 5V41068A is a 2:1 differential clock mux for PCI Express applications. It has very low additive jitter making it suitable for use in PCIe Gen2 and Gen3 systems. The 5V41068A selects between 1 of 2 differential HCSL inputs to drive a single differential HCSL output pair. The output can also be terminated to LVDS.
当前筛选条件