特性
- LP-HCSL outputs; save 10 resistors and 17mm² compared to standard HCSL
- PCIe Gen 1–5 compliance
- 50mW typical power consumption; eliminates thermal concerns
- OE# pin for each output; support DIF power management
- HCSL differential input; can be driven by common clock sources
- Spread spectrum tolerant; allows reduction of EMI
- SMBus-selectable features allow optimization to customer requirements
- Slew rate for each output; allows tuning for various line lengths
- Differential output amplitude; allows tuning for various application environments
- 1MHz to 200MHz operating frequency
- 3.3V tolerant SMBus interface works with legacy controllers
- Selectable SMBus addresses; multiple devices can easily share an SMBus segment
- Device contains default configuration; SMBus interface is not required for device operation
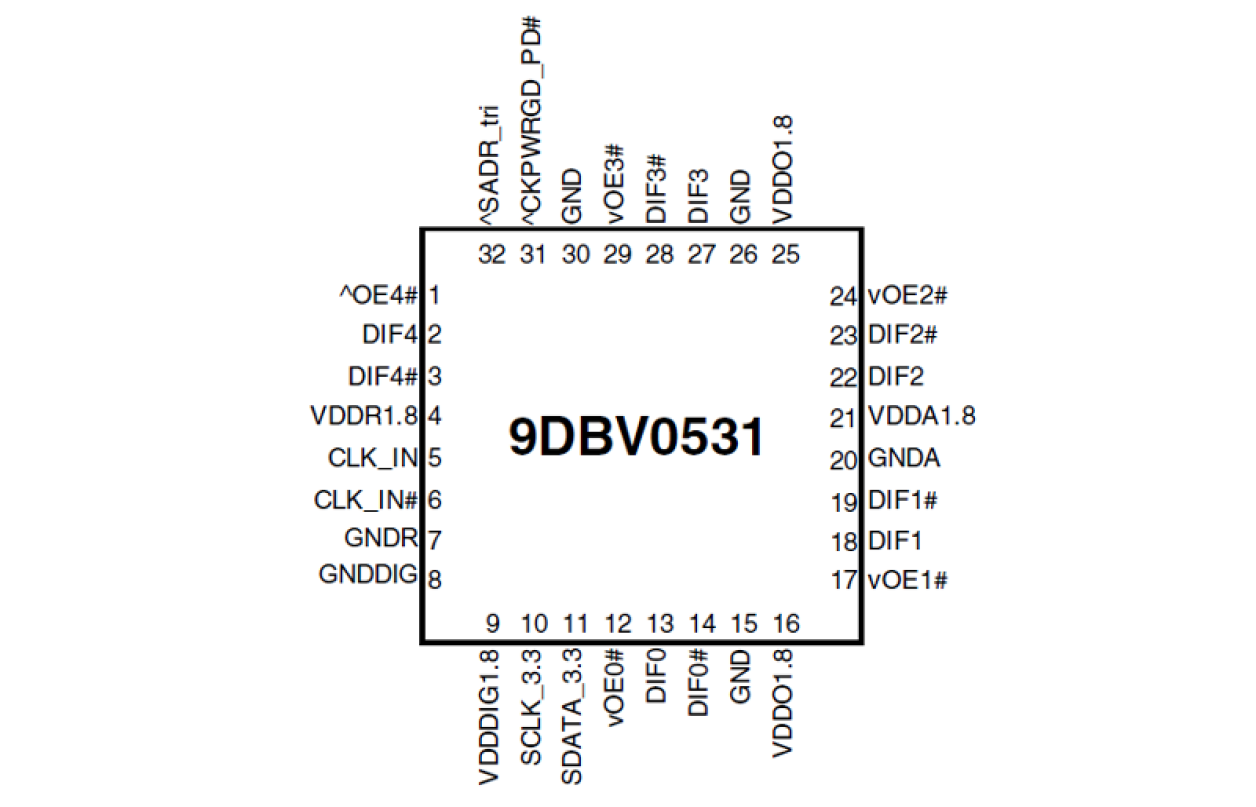
- Space saving 32-pin 5mm x 5mm VFQFPN; minimal board space
描述
The 9DBV0531 5-output 1.8V PCIe fanout clock buffer has five output enables for clock management and three selectable SMBus addresses.
产品参数
| 属性 | 值 |
|---|---|
| Diff. Outputs | 5 |
| Diff. Output Signaling | LP-HCSL |
| Output Freq Range (MHz) | 1 - 200 |
| Diff. Inputs | 1 |
| Diff. Input Signaling | HCSL |
| Accepts Spread Spec Input | Yes |
| Power Consumption Typ (mW) | 45 |
| Supply Voltage (V) | 1.8 - 1.8 |
| Output Type | LP-HCSL |
| Diff. Termination Resistors | 16 |
| Package Area (mm²) | 25 |
| Battery Backup | No |
| Battery Seal | No |
| CPU Supervisory Function POR | No |
| Crystal Frequency Trimming | No |
| Frequency Out Pin | No |
| Inputs (#) | 1 |
| Input Freq (MHz) | 1 - 200 |
| Divider Value | 1 |
| Additive Phase Jitter Typ RMS (fs) | 250 |
| Function | Fanout Buffer |
| Input Type | HCSL |
| Output Banks (#) | 1 |
| Core Voltage (V) | 1.8 |
| Output Voltage (V) | 0.8 |
| Product Category | PCI Express Clocks |
封装选项
| Pkg. Type | Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | Lead Count (#) | Pitch (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VFQFPN | 5.0 x 5.0 x 0.9 | 32 | 0.5 |
应用
- Servers/High-performance computing
- nVME storage
- Networking
- Accelerators
- Industrial control
当前筛选条件