特性
- LP-HCSL output; saves 2 resistors compared to standard HCSL output
- 1.8 V operation; 12 mW typical power consumption
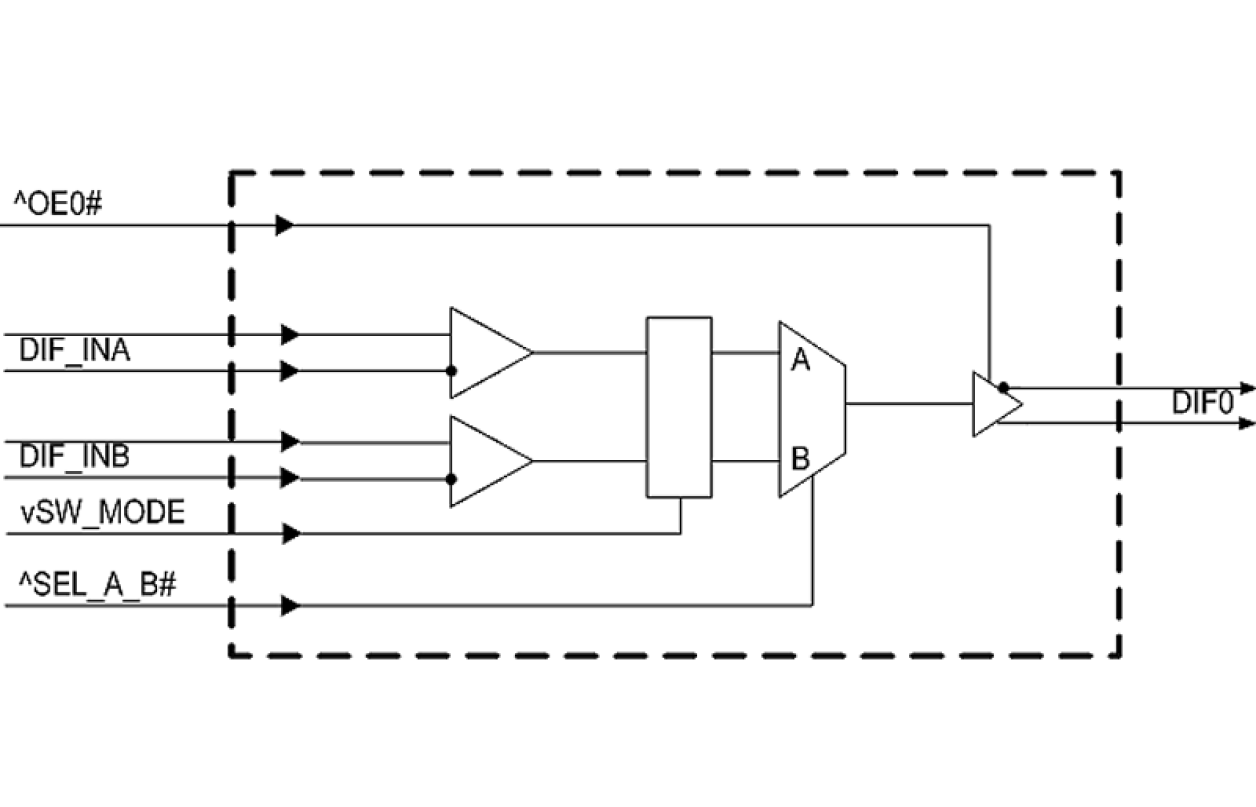
- Selectable asynchronous or glitch-free switching; allows the mux to be selected at power up even if both inputs are not running, then transition to glitch-free switching mode
- Spread spectrum compatible; supports EMI reduction
- OE# pin; supports DIF power management
- HCSL differential inputs; can be driven by common clock sources
- 1 MHz to 200 MHz operating frequency
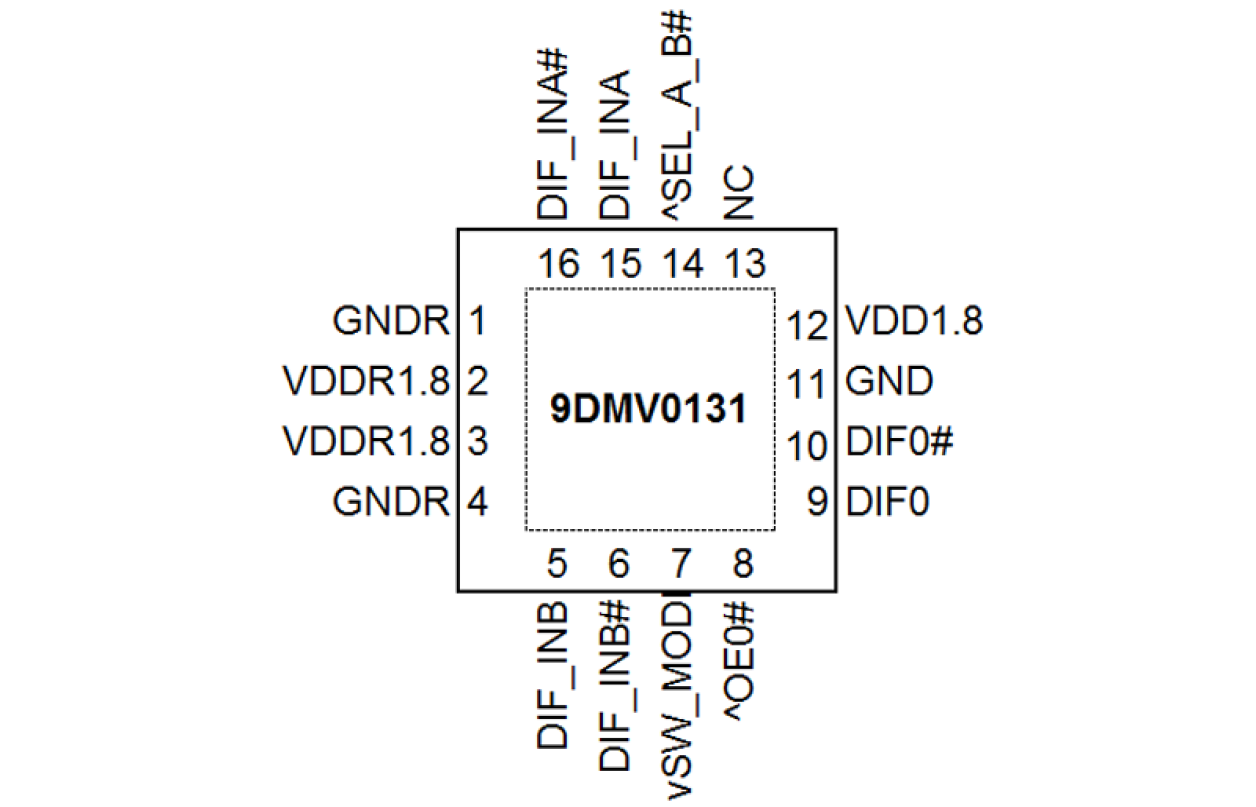
- Space saving 3x3 mm 16-pin VFQFPN; minimal board space
描述
The 9DMV0131 is a member of Renesas' SOC-Friendly 1.8 V Very-Low-Power (VLP) PCIe Gen1–5 family. The output has an OE# pin for optimal system control and power management. The part provides asynchronous or glitch-free switching modes.
当前筛选条件